Intermittent (non-perennial) rivers
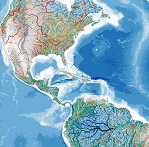
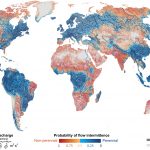
Over half of the world’s rivers cease to flow for at least one day a year
Almost every river network on Earth includes channels that periodically cease to flow, from Himalayan snow-fed creeks to occasionally water-filled Saharan wadis. However, the prevalence, value and fate of non-perennial rivers and streams tend to be overlooked, if not ignored. Through this project, we predict that water ceases to flow for at least one day per year along 51–60 per cent of the world’s rivers by length, demonstrating that non-perennial rivers and streams are the rule rather than the exception on Earth.
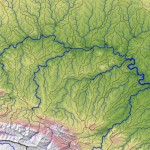
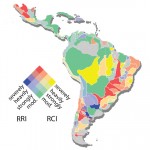
Free-flowing rivers are the freshwater equivalent of wilderness areas
Free-flowing rivers provide crucial habitat for a host of animals, and support the survival of both people and nature around the world. Together with World Wildlife Fund and many colleagues, we conducted a global assessment of the location and extent of the planet’s remaining free-flowing rivers. The results highlight severe degradation, and offer a method for tracking the status of free-flowing rivers over time. A map of free-flowing rivers can be viewed here.
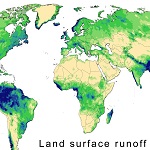
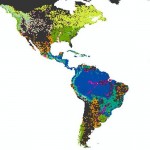
Hydrological data and maps based on Shuttle Elevation Derivatives at multiple Scales
HydroSHEDS is a hydrographic mapping product that provides river and watershed information for regional and global-scale applications in a consistent format. It offers a suite of geo-referenced data sets (vector and raster) at various scales, including river networks, watershed boundaries, drainage directions, and flow accumulations. HydroSHEDS is based on high-resolution elevation data obtained during a Space Shuttle flight for NASA’s Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM).
Global compendium of hydro-environmental sub-basin and river reach characteristics at 15 arc-second resolution
HydroATLAS is a comprehensive database gathering and presenting a wide range of hydro-environmental attributes from existing global datasets in a consistent and organized manner. HydroATLAS is divided in two datasets, BasinATLAS and RiverATLAS, which represent sub-basin delineations (polygons) and the river network (lines), respectively. HydroATLAS offers attributes organized in seven categories: hydrology; physiography; climate; land cover & use; geology & soils; and anthropogenic influences.
Global polygon database of all lakes with a surface area of at least 10 ha
HydroLAKES is a database aiming to provide the shoreline polygons of all global lakes with a surface area of at least 10 ha. Additional attributes for each of the 1.4 million lakes include estimates of the shoreline length, average depth, water volume and residence time. All lakes are co-registered to the global river network of the HydroSHEDS database via their lake pour points.
River routing
Cumulative processes are important determinants of local conditions in river networks. HydroROUT is a set of simulation tools based on HydroSHEDS baseline data that provides routing, tracing and statistical processing within the river network to facilitate eco-hydrological modelling.
Global reservoir and dam database
The Global Reservoir and Dam database (GRanD) contains information regarding 6862 dams and their associated reservoirs, with a total storage capacity of 6197 km3. On the basis of these records, we estimate that about 16.7 million reservoirs larger than 0.01 ha – with a combined storage capacity of approximately 8070 km3 – may exist worldwide, increasing Earth’s terrestrial surface water area by more than 305 000 km2. We find that 7.6% of the world’s rivers with average flows above 1 cubic meter per second, are affected by a cumulative upstream reservoir capacity that exceeds 2% of their annual flow.
River fragmentation and flow regulation
Assessing major impacts of dams
Anthropogenic obstructions such as dams have been shown to decrease hydrological connectivity through barrier effects and to cause alterations of the natural flow, both of which are having very significant impacts on ecological integrity of rivers, wetlands and floodplains as well as on freshwater biodiversity. Using GranD and a set of future dams, we assess current and future legacies of dam construction.
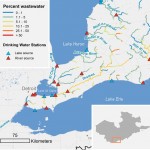
Geospatial contaminant risk assessment
Thousands of industrial and natural chemical substances are released into the environment from household, industrial and agricultural sources, posing significant environmental challenges. We developed a new geospatial contaminant fate model capable of predicting chemical concentrations for a variety of substances from consumer products at scales and with a suitable accuracy to support screening and decision making.
Global river classication
River type classifications can reveal the spatial and hydrological configuration of a river system and can serve as a first-order proxy for large-scale aquatic biodiversity patterns and their related aquatic ecosystem services. The Global River Classification framework (GloRiC) aims to create managable freshwater units based on hydrology, physiography and climate, and geomorphology, supported by expert assessment.
Global inundation mapping
Temporarily or seasonally inundated habitats such as wetlands and floodplains are recognized as irreplaceable biodiversity hotspots. GIEMS-D15 represents water extent at three time scales, making it the first temporally explicit global map of surface water extent.
Global lakes and wetlands database
Global Lakes and Wetlands Database (GLWD) is the combination of the currently best available sources for lakes and wetlands on a global scale (1:1 to 1:3 million resolution). The application of Geographic Information System (GIS) functionality enabled the generation of a database which focuses in three coordinated levels on large lakes and reservoirs, smaller water bodies, and wetlands.
Global waterfall database
HydroFALLS is a global database of validated waterfall points with quality ratings. This product is the first of its kind in terms of scale and spatial coverage at the global scale. The database was created by means of the systematic merging, consolidation and validation of existing waterfall data sets to generate a waterfall point layer.